<2021 KIAS - APCTP>
전자구조계산학교
June 28th(Mon) ~ 30th(Wed), 2021 l Online |
| Program | Home > Program |
프로그램
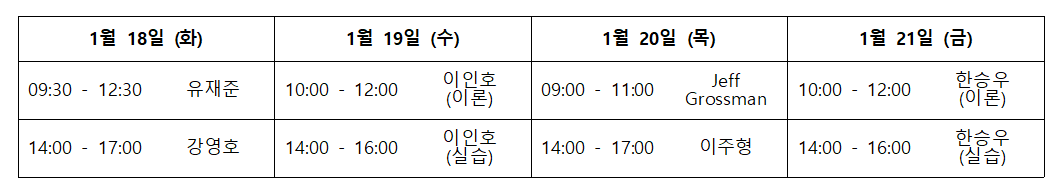
6월 28일 (월)
13:50 ~ 14:00
인사말 유재준 (서울대학교, 전자구조계산학교 교장)
14:00 ~ 14:50
강의제목 Electronic Structure Part I : a grand challenge of theoretical physics with useful applications in many areas of science and technology
강사Prof. R. M. Martin (Univ. of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign/Stanford Univ.)
강의 소개
The role of Electronic Structure in theoretical physics can be appreciated by recalling steps in the development of quantum mechanics from the 1920's to today: Schrödinger’s equation, Dirac’s relativistic quantum mechanics, the Thomas-fermi approximation (a density functional) and essentially exact calculations for 2 electrons in He, all within the first seven years of quantum mechanics. It was clear that somehow one has to deal with the interacting electron many-body problem, and it is awesome that people like Fermi, Hartree, Wigner, Seitz, Slater and others realized ways to extract essential physics using independent-particle methods. Already in the 1930's were developed the basic ideas of almost all the methods used today. Fast forward to today, when we have quantitative methods to predict properties like crystal structures and phonon frequencies to a few percent and a new era where quantitative calculations work hand in hand with experiment, often leading experiment. What was the key step? Density functional theory in 1964 showed how to calculate with remarkable accuracy some (not all!) properties of the full interacting system using independent-particle methods. Other developments like the Car-Parrinello method led to great improvements in calculations that make it feasible to apply the theory to complex systems. The stunning advance of Hohenberg, Kohn and Sham and some of the applications are the topics of this talk.
참고자료
• Richard M. Martin, Electronic Structure: basic theory and practical methods (Cambridge University Press, 2004).
• Richard M. Martin, Lucia Reining and David M. Ceperley, Interacting Electrons: Theory and Computational Approaches (Cambridge University Press, 2016).
14:50 ~ 15:00 Discussion
15:00 ~ 16:00
강의제목 Electronic Structure Part II : a grand challenge of theoretical physics with useful applications in many areas of science and technology
강사 Prof. R. M. Martin (Univ. of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign/Stanford Univ.)
강의 소개
In the second part we return to the problem of interacting electrons and we ask what Kohn-Sham formulation of DFT can and cannot do. One aspect is that in recent years many-body theory and concepts have been increasingly used to develop better functionals that can describe more properties accurately. However, the main issues I will address are qualitative: when is it possible to conclude confidently that one can use independent-particle methods to draw conclusions about the full interacting system? The issues arise in what are often called ``strongly interacting’’ systems and classic questions like "Can DFT describe a Mott insulator?" In addressing such issues, the guiding principle is continuity; the concepts flow from the 1930’s and are best expressed in the work of Landau and Luttinger in the 1950’s and 1960’s. Perhaps surprisingly, temperature plays a key role in understanding the issues. These are topics difficult to cover in a semester course, but I hope to bring out the importance of basic guiding principles alongside the capabilities of DFT.
참고자료
• Richard M. Martin, Electronic Structure: basic theory and practical methods (Cambridge University Press, 2004).
• Richard M. Martin, Lucia Reining and David M. Ceperley, Interacting Electrons: Theory and Computational Approaches (Cambridge University Press, 2016).
6월 29일 (화)
10:00 ~ 11:50
강의제목 Fundamentals of Density Functional Theory
강사 유재준 교수 (서울대, 전자구조계산학교 교장)
강의 소개
We will discuss basic concepts, theories, and methods behind density functional theory (DFT). DFT is a computational quantum mechanical modeling method used in physics, chemistry, and materials science to investigate the electronic structure of many-body systems, particularly atoms, molecules, and condensed phases. We hope to provide a broad perspective on current electronic structure theory and background for practical computations, which serves as starting points of topics in the following lectures: exchange-correlational functional, pseudopotential theory, time-dependent DFT, and many-body perturbation theory. This course aims at the graduate and post-graduate students in theoretical and computational condensed matter physics.
참고자료
• Richard M. Martin, Electronic Structure: basic theory and practical methods (Cambridge University Press, 2004) (ISBN 0 521 78285 6)
• ICTP Workshop “Hands-on Workshop on Density Functional Theory and Beyond: Computational Materials Science for Real Materials”, (6-15 August 2013), http://th.fhi-berlin.mpg.de/sitesub/meetings/DFT-workshop-2013/index.php?n=Meeting.Program
13:00 ~ 14:50
강의제목 스핀-궤도 상호 작용 계산 방법 및 DFT+U 방법론 소개
강사 최형준 교수 (연세대)
강의 소개
본 강의에서는 스핀-궤도 상호 작용을 쑤도포텐셜(pseudopotential) 기반 DFT 계산에서 구현하는 방법론을 설명하고 DFT+U 방법론을 간단히 소개한다. 스핀-궤도 상호 작용은 원자에 속박된 전자의 양자 역학적 상태를 디락 방정식을 사용하여 계산한 후 총 각운동량 J에 의존하는 쑤도포텐셜을 만들고 이 쑤도포텐셜을 밴드 구조 계산에서 스핀에 의존하는 포텐셜로 변형하여 구현된다. 스핀-궤도 상호 작용을 고려하기 위해서는 전자의 헤밀토니안과 파동 함수를 noncollinear-spin 상태로 표현하여야 하며, LDA 또는 GGA의 교환-상관 에너지(exchange-correlation energy)및 교환-상관 포텐셜에서도 noncollinear-spin을 고려하여야 한다. 또한 파동 함수가 운동량 공간에서 가지는 대칭성이 줄어 들 수 있어서, 파동 함수로부터 전자의 공간 분포를 계산하는 과정에도 주의가 필요하다. 한편, DFT+U 방법론은 원자에 강하게 속박된 d 궤도 함수의 전자 상태 계산에 필요하며, 이를 구현하는 방법에 대해 간략히 소개하고, DFT+U 방법에서 힘과 stress의 계산식과 계산 결과에 대해 소개한다.
참고자료
· S. Y. Park and H. J. Choi, First-principles calculation of atomic force in the LSDA+U formalism. Phys. Rev. B 80, 155122 (2009)
· S. Y. Park and H. J. Choi, First-principles calculation of stress tensor in the LSDA+U formalism. Phys. Rev. B 94, 245126 (2016)
15:30 ~ 17:20
강의제목 DFT+U 계열의 방법론 이해하기
강사 한명준 교수 (KAIST)
강의 소개
본 강의에서는 ‘DFT+U’ 계열 방법론에 대한 기본적인 이해를 바탕으로 다음과 같은 질문들을 생각해 보고자 한다: (1) DFT+U/DMFT 등과 같은 방법론은 왜, 언제, 어떻게 사용해야 하는가? (2) 이는 hybrid-DFT 등 다른 유사 방법론과는 어떻게 다른가? (3) DFT+U/DMFT 방법론은 여러 다른 종류의 구체적인 함수 꼴(functional)로 표현된다. 예를 들어 FLL (fully localized limit), AMF (around the mean field) 등이 있는데, 이들은 대부분의 DFT 소프트웨어 패키지들에 input option으로 선택 가능하다. 즉, 실제 연구에서는 이들 가운데 하나를 선택하여 계산을 수행하게 되는데, 이들은 어떤 차이점이 있으며 이 함수 꼴들이 서로 다른 결과를 주는 경우 우리는 그 결과를 어떻게 이해해야 하는가? (4) 그 외에도 Hubbard U, Hund J 등 인자(parameter) 의존성, double-counting, spin density 등의 이슈를 다룬다.
참고자료
· Anisimov, V. I., Zaanen, J. & Andersen, O. K. Band theory and Mott insulators: Hubbard U instead of Stoner I. Phys. Rev. B 44, 943 (1991).
· Anisimov, V. I., Aryasetiawan, F. & Lichtenstein, A. First-principles calculations of the electronic structure and spectra of strongly correlated systems: the LDA + U method. J. Phys.: Condens. Matter 9, 767 (1997).
· Chen, J., Millis, A. J. & Marianetti, C. A. Density functional plus dynamical mean-field theory of the spin-crossover molecule Fe(phen)2(NCS)2. Phys. Rev. B 91, 241111 (2015)
· Park, H., Millis, A. J. & Marianetti, C. A. Density functional versus spin-density functional and the choice of correlated subspace in multivariable effective action theories of electronic structure. Phys. Rev. B 92, 035146 (2015)
· Chen, H. & Millis, A. J. Spin-density functional theories and their +U and +J extensions: A comparative study of transition metals and transition metal oxides. Phys. Rev. B 93, 045133 (2016).
· Ryee, S. & Han, M. J. The effect of double counting, spin density, and Hund interaction in the different DFT+U functionals. Sci. Rep. 8, 9559 (2018).
6월 30일 (수)
09:00 ~ 10:00
강의제목 Theory of electric polarization: Berry phases and Wannier functions
강사 Prof. David Vanderbilt (Rutgers)
강의 소개
In this talk, I will review the theory of electric polarization in insulating materials from two apparently different but ultimately equivalent points of view. The first formulation is in terms of Berry phases of Bloch wave functions, while the second is in terms of localized Wannier functions. Some conceptual issues, notable the presence of a quantum of uncertainty in the polarization, will be discussed. The implementation of these methodologies in first-principles density-functional calculations will also be described.
10:00 ~ 11:00
강의제목 Theory of ferroelectric and piezoelectric materials
강사 Prof. David Vanderbilt (Rutgers)
강의 소개
Ferroelectrics are materials in which electric dipole moments spontaneously order to generate a macroscopic electric polarization, in analogy to the spontaneous magnetization of ferromagnets. Because ferroelectric domains can be read and written electrically, they have potential advantages for electronic memory technologies. Ferroelectrics are typically also piezoelectrics, i.e., materials in which strains induce electric charges and vice versa. Such materials are in widespread use in transducer applications ranging from medical ultrasound to marine sonar. In this talk, I will describe applications of the theory of polarization to a variety of ferroelectric and piezoelectric materials, starting with the well-established perovskites and then exploring some more novel materials that have been the subject of recent investigations.
13:00 ~ 14:50
강의제목 시간의존 밀도 범함수 이론의 소개
강사 방준혁 교수 (충북대)
강의 소개
밀도 범함수 이론(density functional theory)에 기반 한 제일원리 계산 방법은 지난 수십 년 동안 급속한 발전을 이룩해 왔으며, 물질들의 양자역학적 특성을 이해하는데 중요한 이론적 방법론으로 자리 잡았다. 하지만 밀도 범함수 이론은 전자의 바닥상태를 가정한 이론으로 주로 정적인 바닥상태 특성을 이해하는데 적용되어져 왔다. 하지만 많은 흥미있는 물리 현상들은 들뜬 상태 전자들의 다양한 동역학적 과정들에서 나타나며, 이런 들뜬 상태 전자 동역학에 대한 이론적 연구 방법은 여전히 초기 단계에 머물고 있다. 본 강의에서는, 물질 내 전자의 동역학적 특성을 분석하기 위한, 시간의존 밀도 범함수 이론(time-dependent density functional theory)을 소개하고자 한다. 우선 시간의존 밀도 범함수 이론의 기본이 되는 Runge-Gross theorem과 van Leeuwen theorem을 소개하며, 시간의존 밀도 범함수 이론에서의 exchange-correlation 포텐셜의 특성을 설명한다. 이 이론을 실제 계산에 적용하는데 필요한 수치 계산 방법들을 설명하고, 이 방법을 활용한 몇 가지 연구 결과들을 소개하고자 한다.
참고자료
• C. A. Ullrich, Time-Dependent Density-Functional Theory: Concepts and Applications (Oxford University Press, 2012) (ISBN 978 0 19 956302 9)
• M. A. L. Marques et al., Lecture Notes in Physics 837: Fundamentals of Time-Dependent Density Functional Theory (Springer, 2012) (ISBN 978 3 642 23517 7)
• 방준혁, Time-Dependent Density Functional Theory를 이용한 물질 내 전자 동역학 연구, 물리학과 첨단기술 2017년 10월, 22페이지 (https://webzine.kps.or.kr/?p=4&idx=39)
• 방준혁, 2차원 물질 내 들뜬상태 전자 동역학, 물리학과 첨단기술 2020년 9월, 15페이지 (https://webzine.kps.or.kr/?p=5_view&idx=16471)
15:00 ~ 16:50
강의제목 Photon-dressed states and nonlinear optical responses: Full ab initio simulations based on time-dependent density functional theories
강사 박노정 교수 (UNIST)
강의 소개
In this school, we present several working examples of light-matter hybrid states, or the material states under a strong driving field, that can be computed with the real-time evolution of time-dependent density functional theory (rt-TDDFT). Starting from the text book notations of time-dependent Schrodinger equation, we explore how materials states, coupled with a strong or weak light field, can be computed by implementing the light field into the vector potential in the kinetic part of the Kohn-Sham Hamiltonian. The aspects of computation algorithm, the time-evolution technique in the framework of plane-wave pseudopotential theories, will be shortly touched, but the main part of the talk will be given to physical examples. As a response to a weak static uniform electric field, we calculated the intrinsic conductivity that corresponds to the topological invariants of quantum Hall or quantum spin Hall insulators. In response to a strong field, we challenge to computing high harmonic responses of insulators. Specifically, we present that the nonlinear transverse responses of insulators can be calculated. In a sense, this second-order Hall effect is analogous to the nonlinear Hall effect of noncentrosymmetric metals, mediated by the Berry curvature dipole, and the circular photogalvanic effect of insulators. The same computation method will be applied to the dynamics of SOC-split bands coupled by a strong external field. Together with the computation results, we suggest open questions whether the Rabi oscillation patterns, captured by the TDDFT calculations, can be rigourously matched with the polariton state, and such a photon-dressed dynamical states can accommodate real spin dynamics in terra hertz ranges.
참고자료
· D. B. Shin et al., Unraveling Materials Berry Curvature and Chern Numbers from Real-Time Evolution of Bloch States, Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 116, 4135, (2019).
· Sodemann and L. Fu, Quantum Nonlinear Hall Effect Induced by Berry Curvature Dipole in Time-Reversal Invariant Materials, Phys. Rev. Lett. 115, 21 (2015).
· Q. Ma et al., Observation of the Nonlinear Hall Effect under Time-Reversal-Symmetric Conditions, Nature 565, 337, (2019).
· J. E. Sipe and A. I. Shkrebtii, Second-Order Optical Response in Semiconductors, Phys. Rev. B 61, 5337, (2000).
· S. Y. Xu et al., Electrically Switchable Berry Curvature Dipole in the Monolayer Topological Insulator WTe2, Nat. Phys. 14, 900, (2018).
